Three lasers Raman Microscope
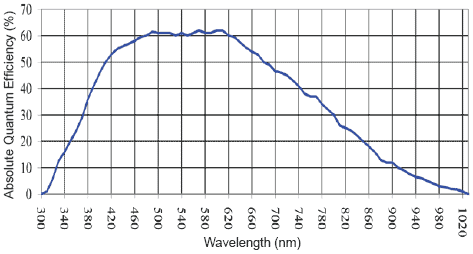
Lasers at 780 nm to 785 nmThe fluorescence of the minerals in rocks can obscure the signal so that any Raman spectrum can't be observed in some cases. One of the solution to this problem is to change the wavelength of the laser. At higher wavelength like 780 nm, the fluorescence could be lower. However, at this high wavelength, the Raman signal is much weaker and the sensitivity of silicon CCD is also lower above 700 nm. As a result, the spectra intensities are generally low so the use of a 780 nm laser is not recommended for a first Raman project.
As can be seen on the image above (graph from Sony), the sensitivity of the camera is only 1/3 of the response at 500 nm ! |
|
|
|
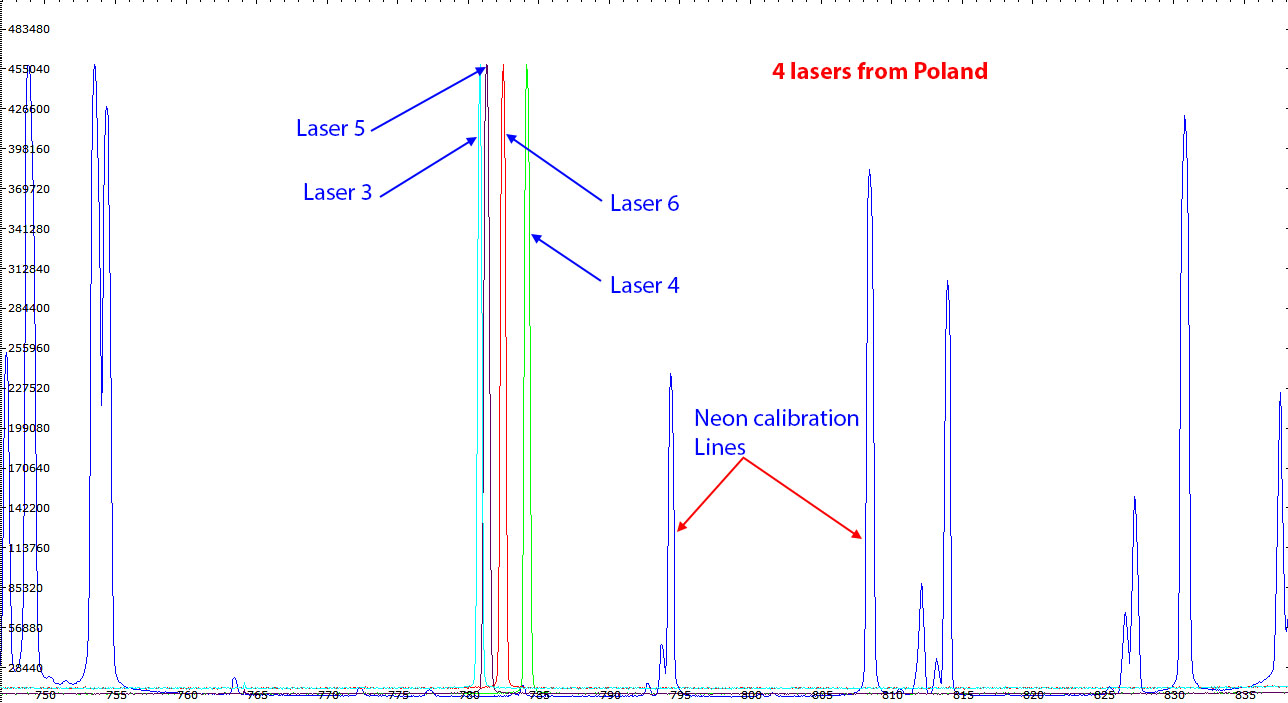
Above, six lasers I have found on eBay from China and from Poland. All are diode lasers, they have a power of 120mW. Power supply 5V. The laser driver is included.
|
|
|
| Spectra of 4 different diode lasers. The laser line of the diodes can be in the range 780 to 785 nm or more. This spread of the wavelengths according to the laser unit is far beyond the transmission width of the narrow band pass filters generally used for Raman spectroscopy. Moreover the laser line position is sensitive to the temperature as described below. It is thus necessary to control the laser temperature with precision to adjust the laser wavelength into the band of the laser cleaning filter. Neon lines have been added in this figure for wavelength calibration.
|
|
|
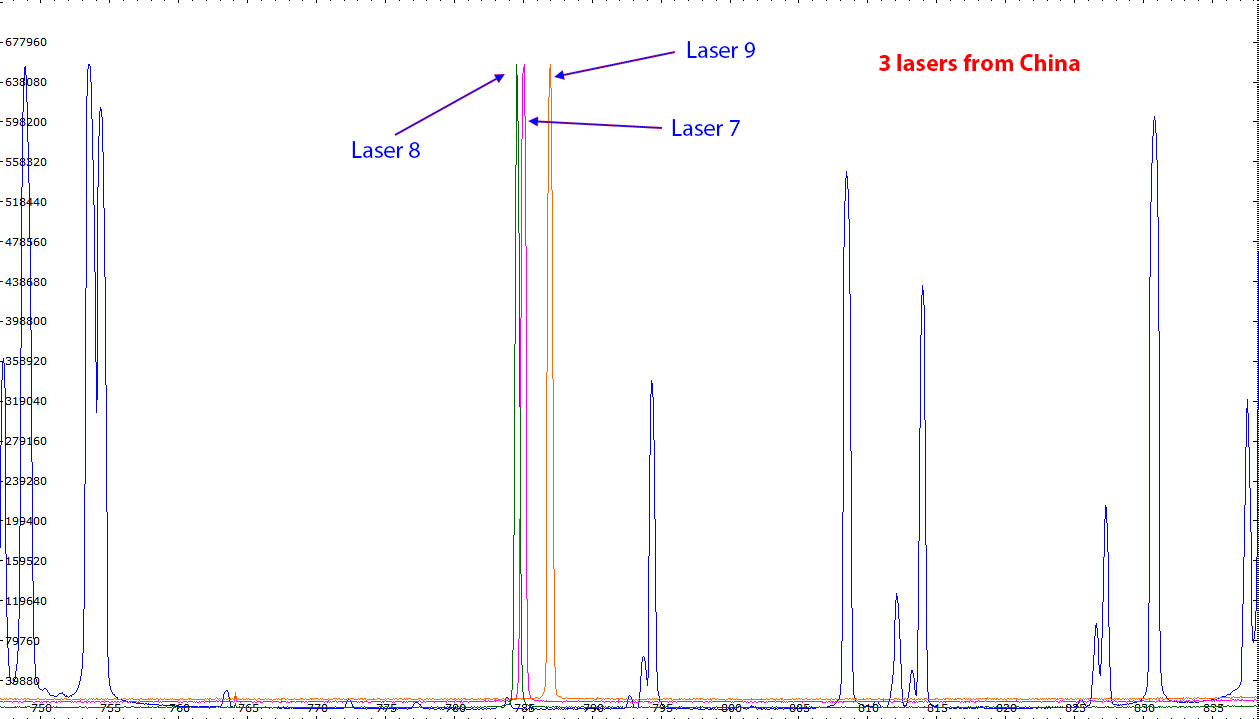
| Laser spectra of 3 laser diodes from different origin.
|
|
|
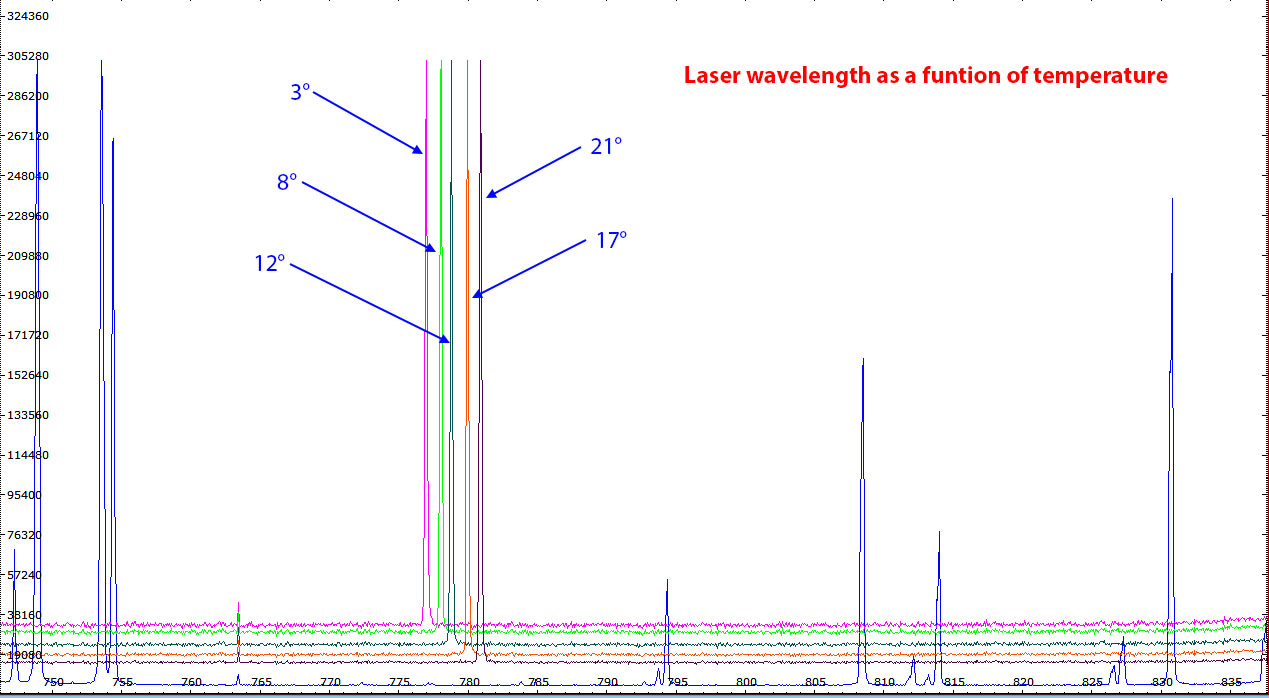
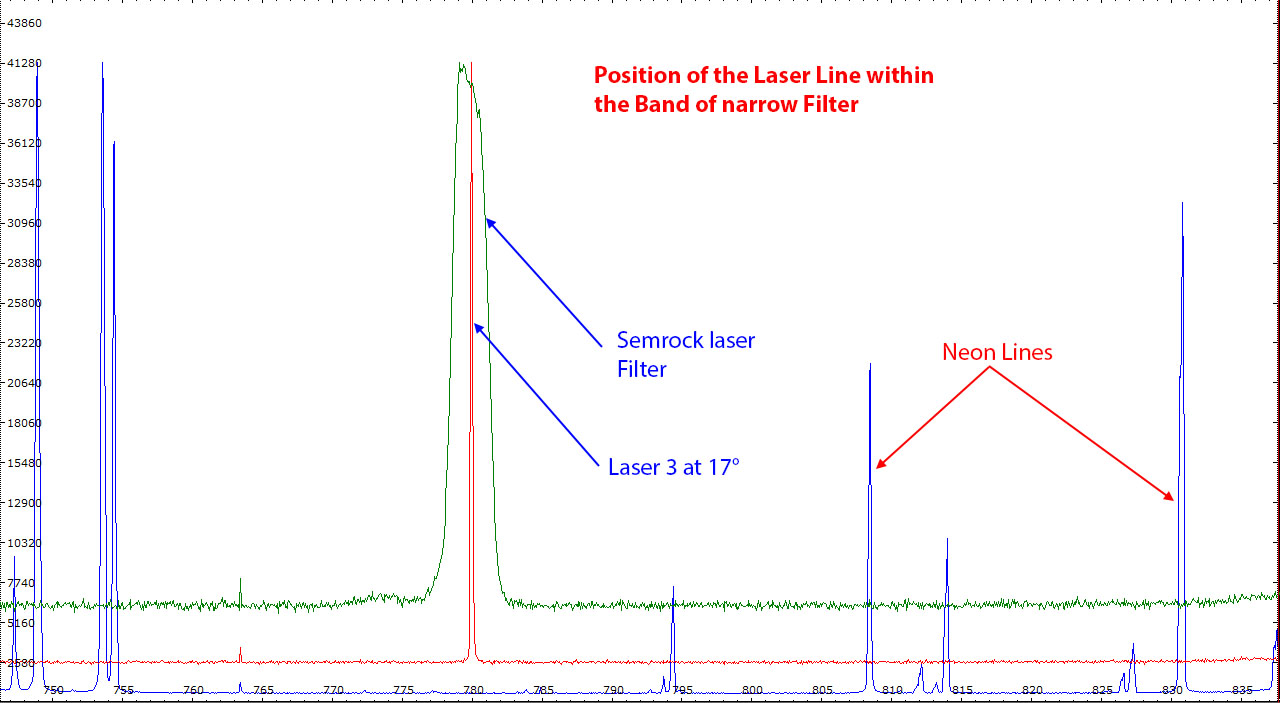
| As mentioned above, the laser line is sensitive to the temperature and goes toward lower wavelength as the temperature is decreased. The wavelength shift is approximately 0.2 nm per degree. So the best laser is one with a line wavelength positioned slightly above the band pass of the cleaning filter that could be adjusted by a cooling down of the laser temperature by a few degrees. The laser chosen to set up the Raman was laser 3. Its wavelength is slightly above 780 nm.
|
|
|
| Laser 3 wavelength position can be adjusted in the middle of a Semrock 780 nm laser cleaning filter by lowering the laser temperature from 20° to 17° as can be seen above.
|
|
|
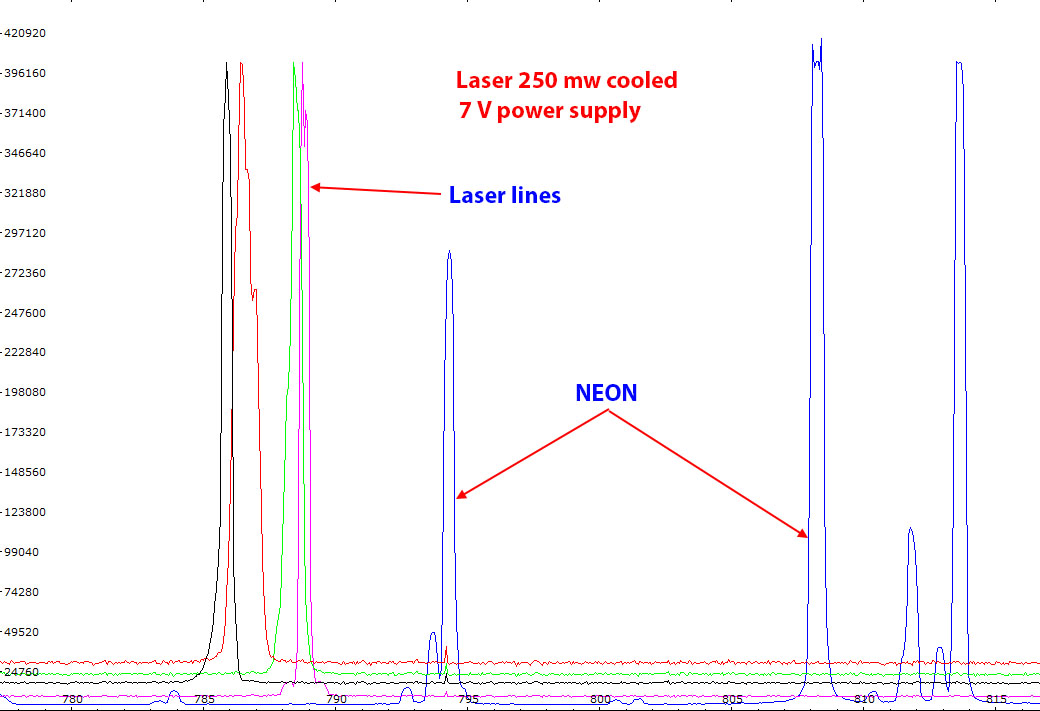
| I have also tried a higher power diode laser (250 mw) but I found this laser unsuitable for Raman due to the erratic line shape and position during time as illustrated above. The wavelength is far away from the 780 nm target of my filter. Of course, it is always possible to select other cleaning and edge filters, for instance 785 nm, but those filters are much more expensive than the low cost lasers I'm using for this project.
|