NIR reflectance spectra of chemical salts, acids,sugar and flour
| Reflectance spectrum of ammonium chloride. The spectrum illustrates the overtones and combination bands of the N-H bond. |
 |
|
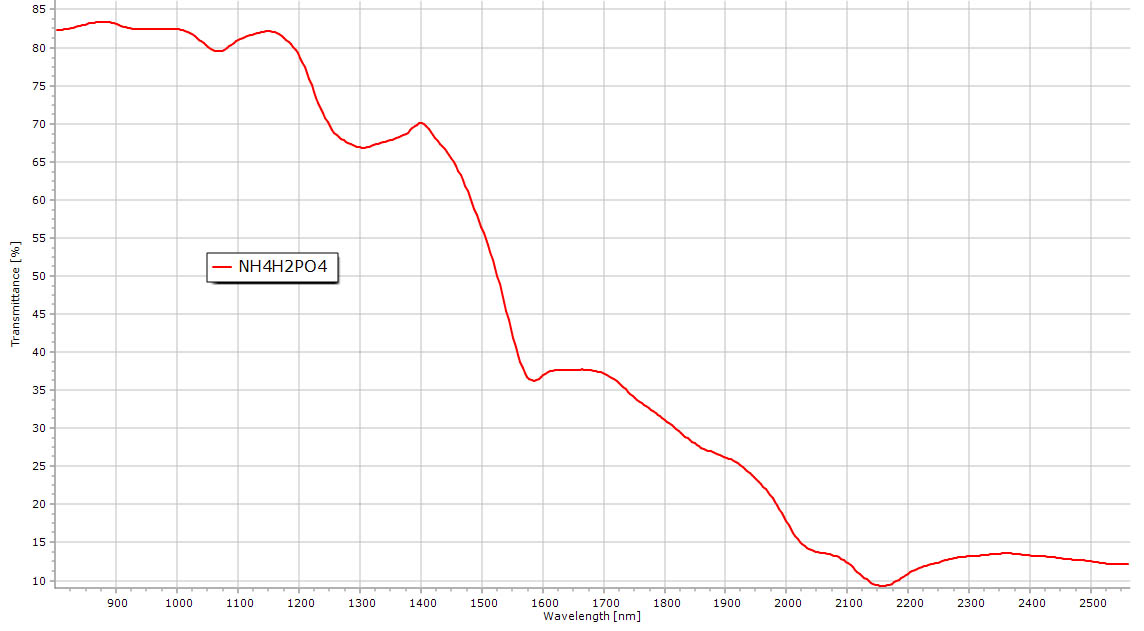
Reflectance NIR spectrum of ammonium di-hydrogen phosphate. Compared to NH4Cl above, the same NH features are present in the phosphate spectrum although much less resolved. OH from the phosphate ion seems to be very broad. |
 |
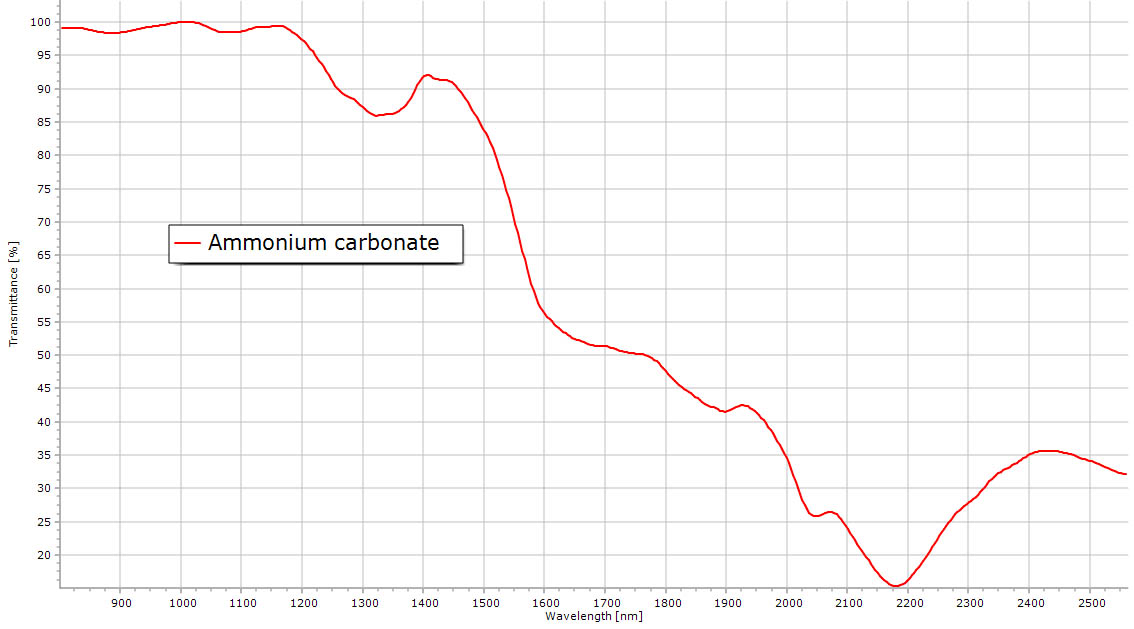
| Ammonium carbonate NIR spectrum. |
 |
|
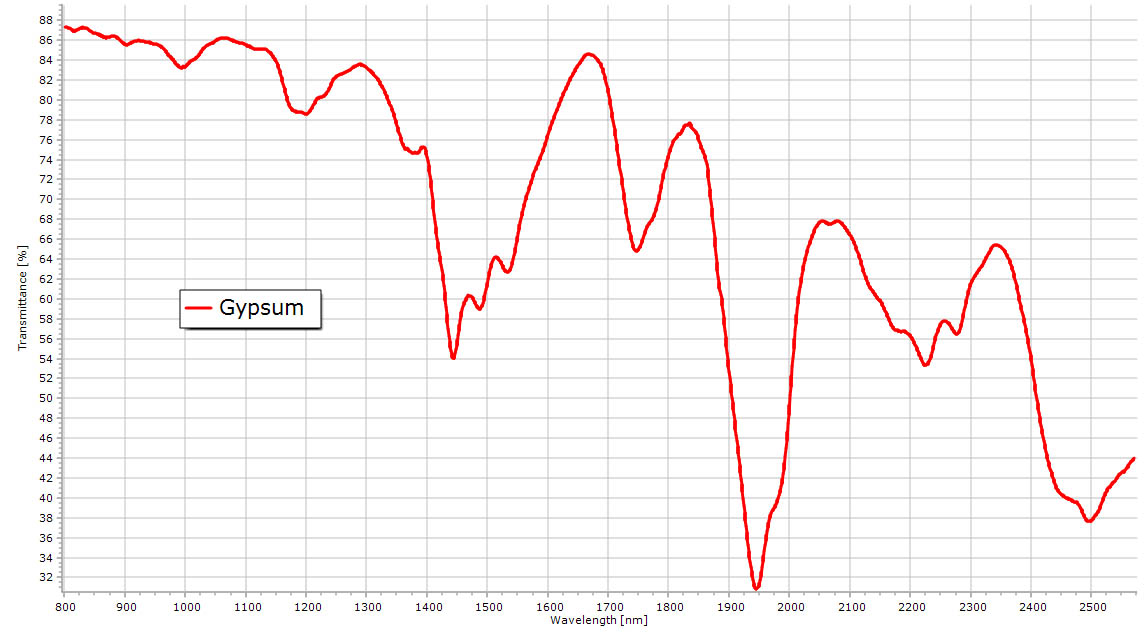
The six spectra below show the features of crystal water in salts. Reflectance NIR spectrum of a gypsum powder. Some transmission spectra with the microscope spectrometer can also be seen here. The main peak of water can be recognized here. More details are visible in the solid gypsum spectrum compared to water. |
 |
|
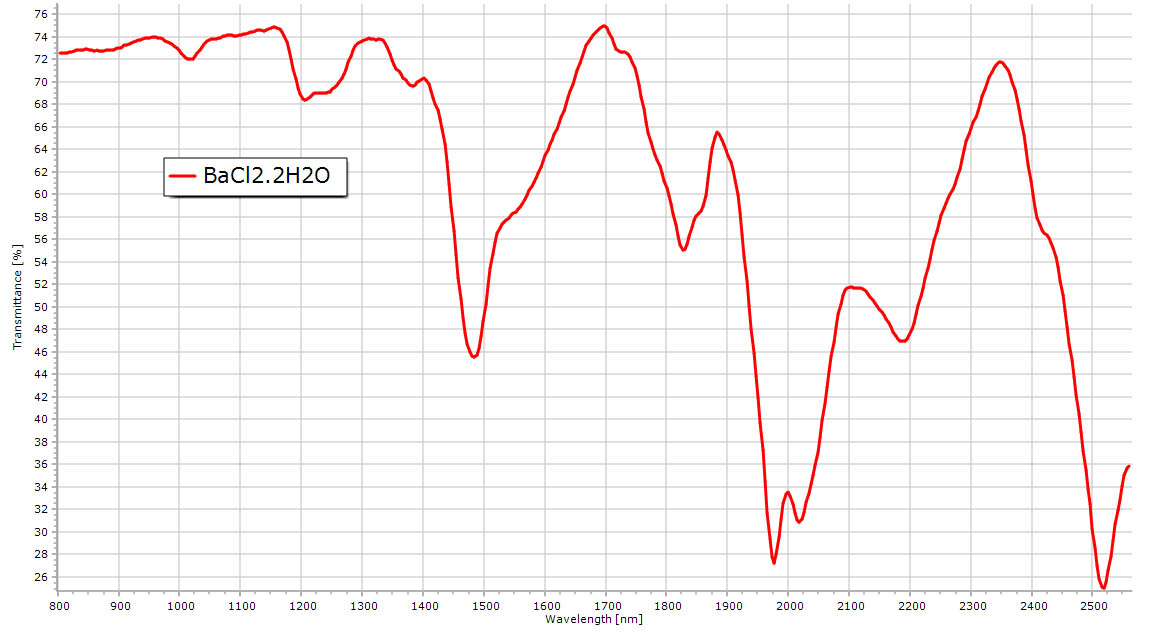
Baryum chloride NIR powder spectrum. Same water features visible in the spectrum compared to gypsum but at slightly different positions. |
 |
| Hydrated copper chloride spectrum. Water peaks similar to the preceding two spectra with less details. The broad absorption at 800 nm is due to the crystal field transitions in the copper ion. |
 |
|
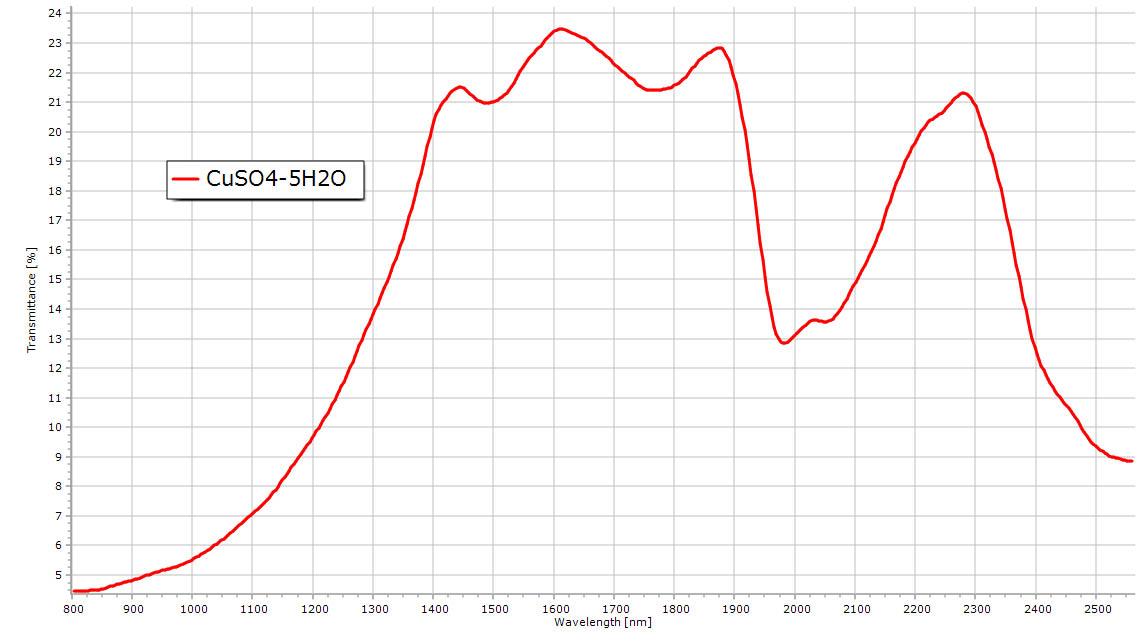
Copper sulfate spectrum. Water absorptions still visible but less pronounced. Same copper crystal field absorption at 800 nm. |
 |
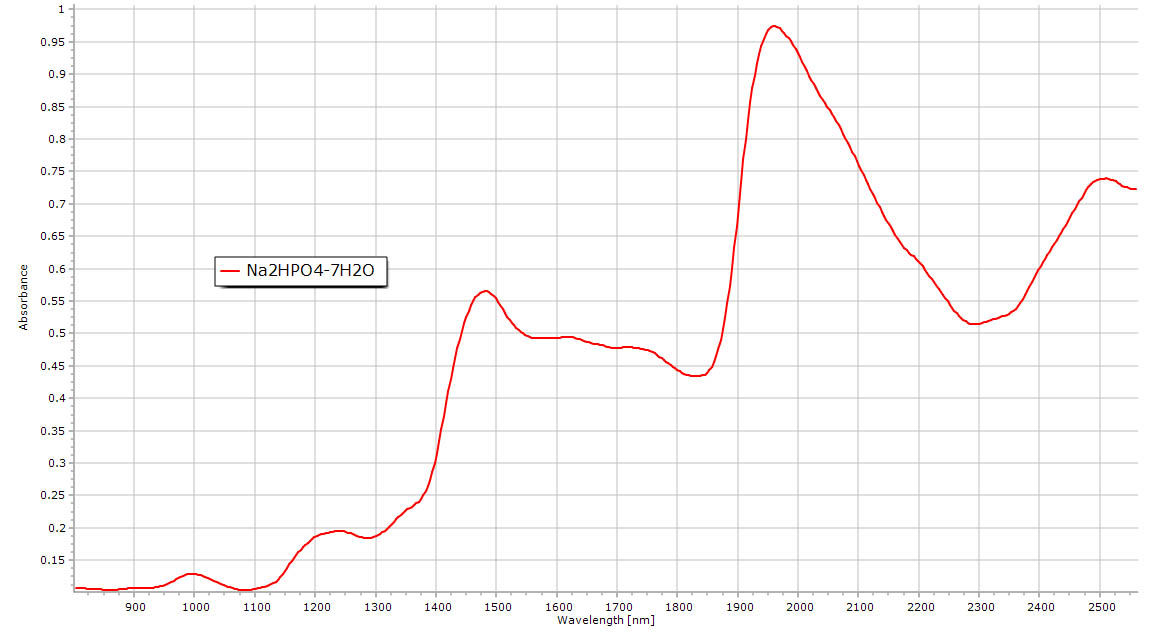
| Hydrated sodium phosphate salts. Mixed spectrum of water and acidic OH linked to phosphorus. Faint water features still present but obscured by the acid OH. |
 |
 |
| Some organic acids NIR spectra combining CH bonds overtones and acidic carboxylic acid. Aliphatic and phenolic OH are also present in some examples. Benzoic acid is characterized by a rich good resolved spectrum. |
 |
| Salicylic acid with carboxyl and phenolic hydrogen. Similarities with the benzoic acid spectrum but less resolved. |
 |
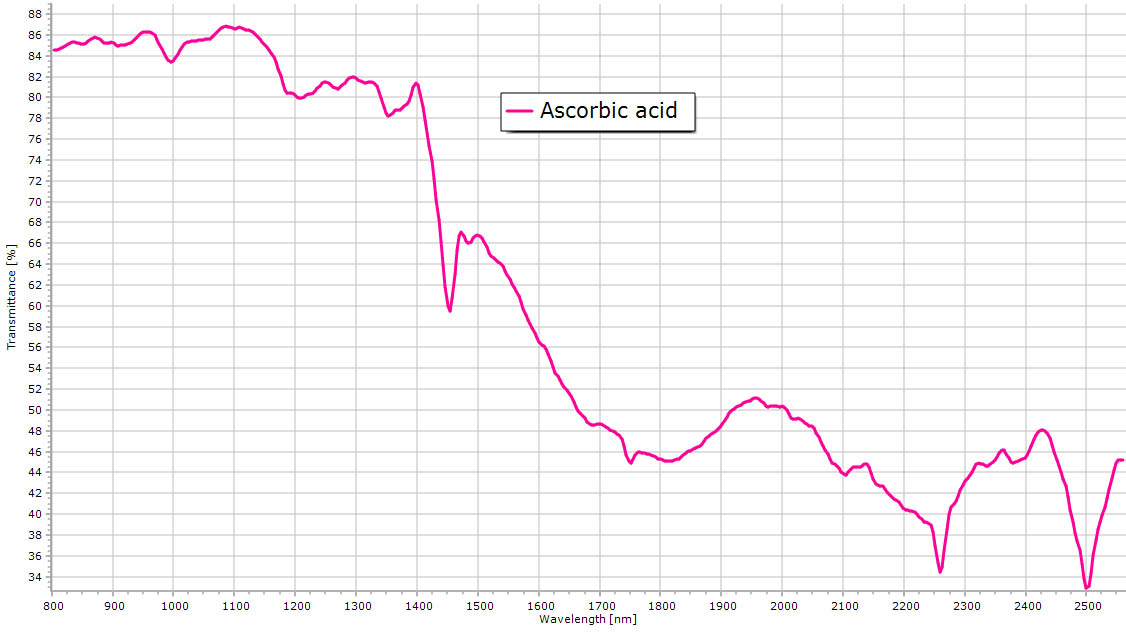
| Ascorbic acid. |
 |
| Tri-carboxylic with alcohol group citric acid. |
 |
|
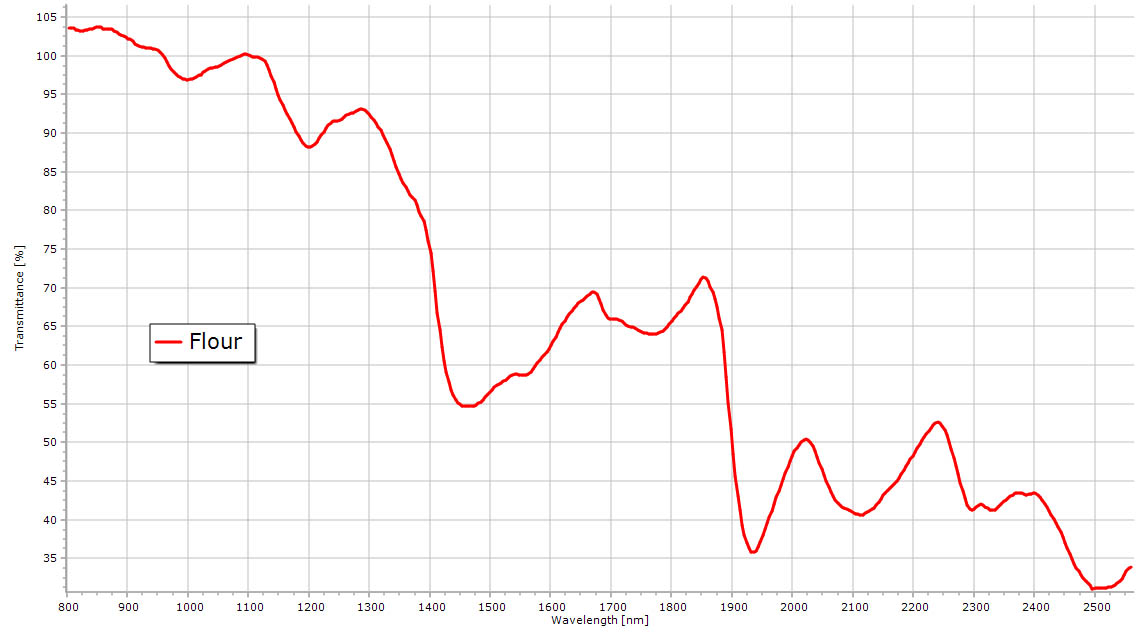
Household flour NIR spectrum. |
 |
|
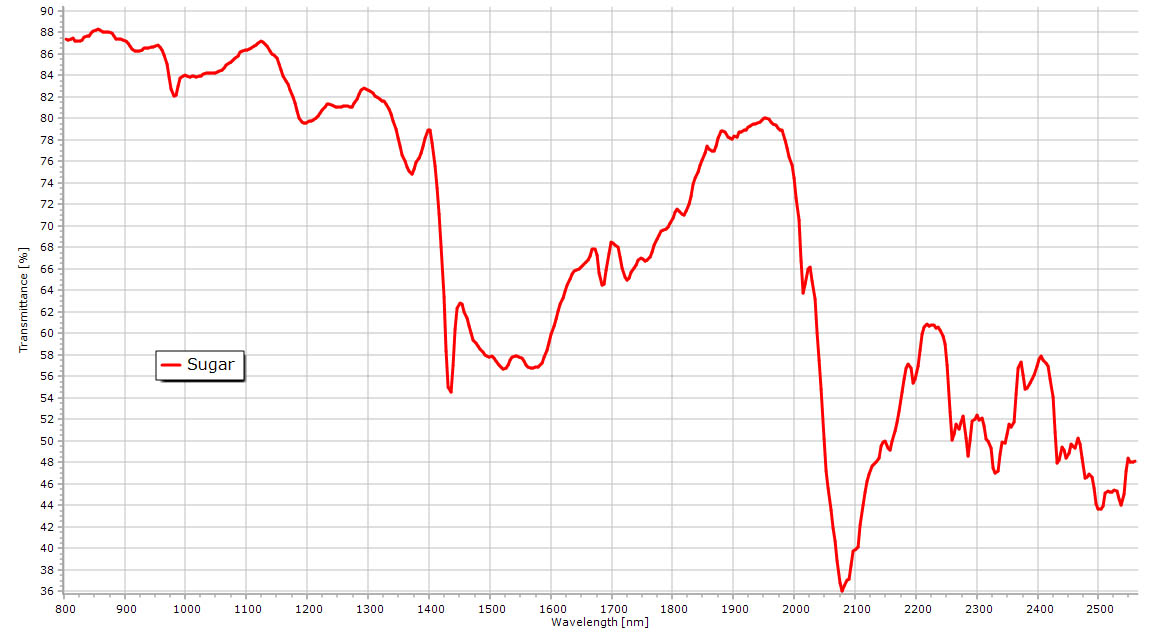
Rich NIR spectrum of powder sugar with CH and OH overtones. |
 |